JMX Administration
Enabling JMX
JMX support is disabled by default. To use it, it must be enabled in the Management Swiftlet.
MBeans
SwiftMQ wraps the router's management tree with MBeans. It creates one MBean per Entity. The object names of the MBeans are equal to the CLI context names. It is configurable whether these names are created in a grouped fashion or as flat names. It depends on the JMX administration tool whether it is able to form a hierarchy like in SwiftMQ Explorer or not. jConsole, the tool delivered with the JDK, is able and we will use it here as an example.
JMX Management with jConsole
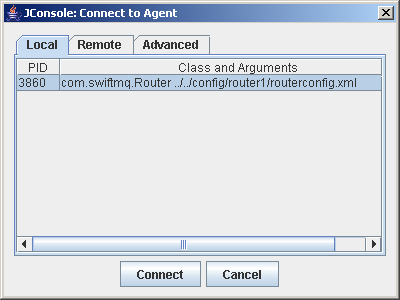
Start the SwiftMQ Router with JMX enabled. Then start jConsole. If JDK 1.5 is in your path, a simple
jconsoleshould do it. jConsole discovers the running JVMs and displays a connect dialog for those which have JMX access enabled:
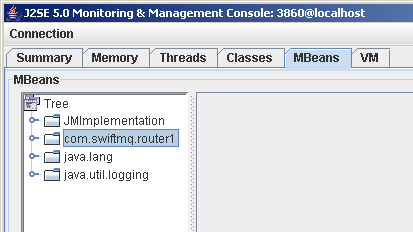
After connecting switch to the MBeans tab:
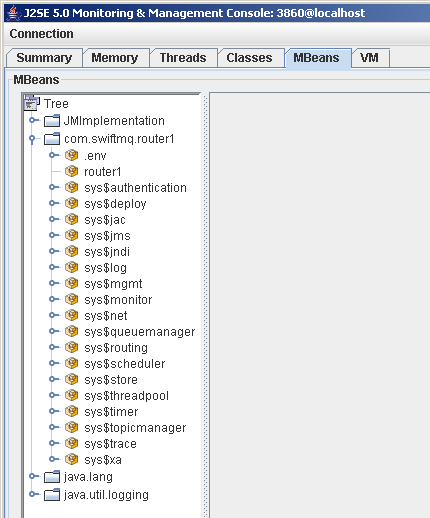
Under the left tree, you'll see the different JMX domains. Your SwiftMQ Router is under domain com.swiftmq. appended with the router name. Expand the SwiftMQ domain node and you will see the router's management tree just like in SwiftMQ Explorer:
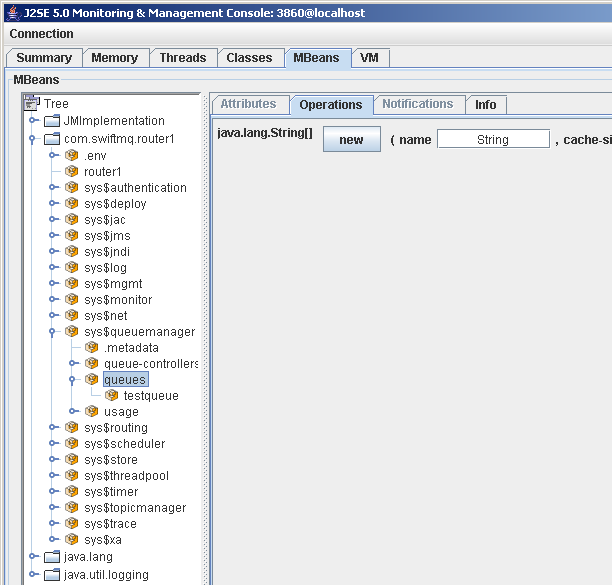
You can now do everything just like in SwiftMQ Explorer. For example, to create a new queue, go to sys$queuemanager, queues and click on the right Operations tab. Then fill in the parameters of the newoperation and click the new button:
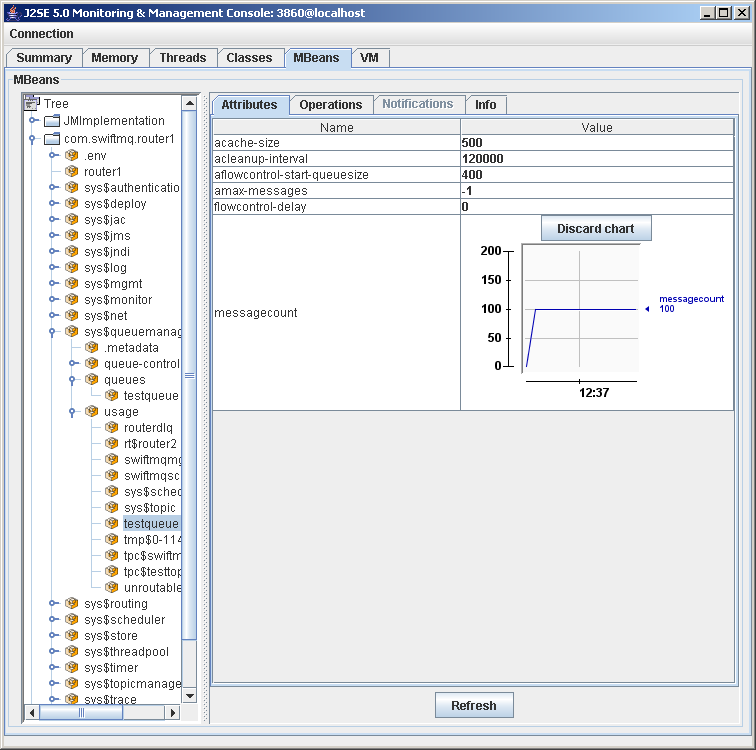
To view the message count of a queue, go to sys$queuemanager, usage, click the queue name, and then at the Attributes tab. Click on messagecount to display a chart:
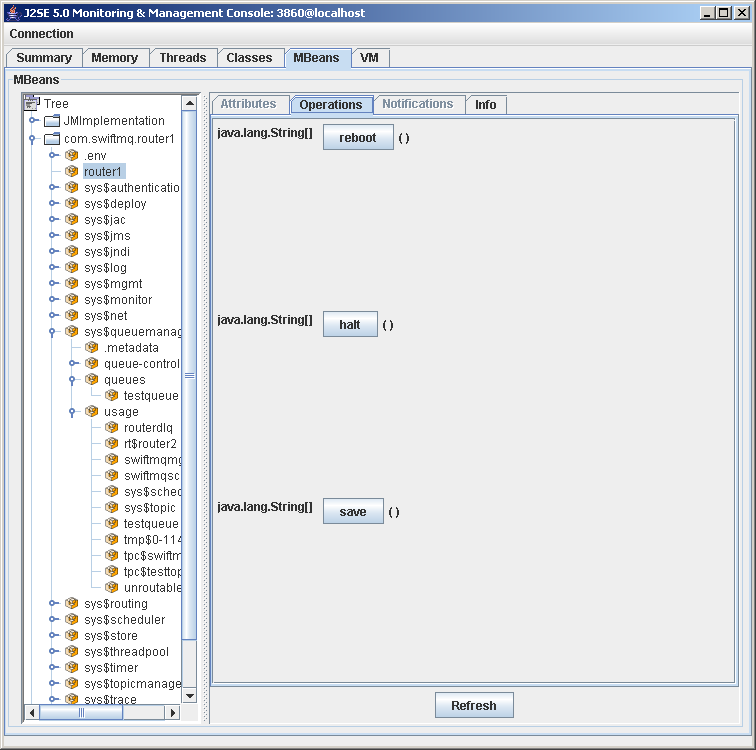
There is one special MBean to expose router-specific commands like halt, reboot, save. This MBean's object name is the router's name. Click on this node and then on the Operations tab to see these commands: