Management Swiftlet
Introduction
The Management Swiftlet is the management facility of a SwiftMQ router and the server-side component for the administration tool CLI.
Protecting Access
A SwiftMQ router is manageable from a SwiftMQ administration component if the component has a send grant on the queue swiftmqmgmt of the particular router because this queue is the inbound queue of the Management Swiftlet to process management requests. Since authentication can be granted on any router in a SwiftMQ router network, everybody can administer a SwiftMQ router if his local router grants access to the management queue on a remote router.
Access to the Management Swiftlet can be password protected and administration tools have to perform an additional authentication step to get access to the protected router.
Protecting access is quite easy. One has to set the attribute authentication-enabled to true and has to specify a password via the attribute password.
Example:
<swiftlet name="sys$mgmt" authentication-enabled="true" password="h7kyxZZu"/>With CLI (or the CLI Admin API) the command authenticate has to be used to authenticate access against a protected Management Swiftlet:
Example:
router1> authenticate h7kyxZZu
router1>_Admin Roles
Admin Roles include or exclude specific grants on the Management Tree of a SwiftMQ Router. With this, it is possible to have different types of administrators or operators who will only see parts of the Management Tree, for example, administrators that can only see and configure particular Swiftlets or operators who will only be able to monitor the store and message counts of particular queues without the right to modify data.
Enabling Admin Roles
Admin Roles need to be enabled at the Management Swiftlet. For compatibility reasons they are disabled by default. To enable Admin Roles, set attribute admin-roles-enabled to true:
<swiftlet name="sys$mgmt" admin-roles-enabled="true">Configuration
Admin Roles are defined per JMS user and consist of a set of context filters. A context filter has the following attributes:
Attribute | Meaning |
|---|---|
name | A unique name that is used for lexical ordering of the filter, e.g. "01", "02" etc. Filters are applied in this order. |
cli-context-predicate | A SQL Like predicate that is applied against CLI contexts, e.g. "/sys$queuemanager/usage/%/messagecount" |
type | The type of this filter: "include" (default), "exclude". "include" grants the context, "exclude" revokes it. |
read-only | Marks a CLI context attribute as read-only, even it is not. Default is false. |
granted-commands | A list of SQL Like predicates, separated by blanks, which is applied against the available commands of this context. |
An empty Admin Role has all CLI contexts excluded and all commands disabled.
Admin Roles are defined in the Management Swiftlet configuration.
<swiftlet name="sys$mgmt" admin-roles-enabled="true">
<jmx enabled="true">
<mbean-server/>
</jmx>
<message-interface/>
<roles>
<role name="admin">
<context-filters>
<context-filter name="01" cli-context-predicate="%" granted-commands="%"/>
</context-filters>
</role>
</roles>
</swiftlet>How to address CLI Contexts
The value in attribute cli-context-predicate is a SQL Like predicate. Wildcards in this predicate are % for any character and _ for a single character. The escape character is \. This predicate is matched against all CLI contexts. The CLI context starts with a / followed by the Swiftlet name and subsequent nodes in the hierarchy of the Management Tree.
Examples:
/sys$jms/listeners/%contains all JMS listeners/.env/router-memory-list/router1/%contains the current memory usage of a router/sys$queuemanager/queuesspecifies only the entity list where queues are defined but not the queues itself/sys$queuemanager/queues/%/cache-size-dbcontains all defined queues but access is granted to the attributecache-size-kbonly
For example, to allow a user to create and delete queues, the new and delete commands must be granted to context /sys$queuemanager/queues. In order to view the declared queues and to change property values for those queues, the set commands need to be granted to context/sys$queuemanager/queues/% .
Example:
<context-filter name="01" cli-context-predicate="/sys$queuemanager/queues"
granted-commands="new delete"/>
<context-filter name="02" cli-context-predicate="/sys$queuemanager/queues/%"
granted-commands="set"/>A special node is the top-level router node. This node owns the router commands such as halt, save, reboot etc. To grant these commands, the / plus router name needs to be specified as CLI context predicate. For router1 this would be /router1. The following example shows how to grant only the save and reboot commands:
<context-filter name="01" cli-context-predicate="/router1"
granted-commands="save reboot"/>Examples
Full Admin Rights
This role grants full rights on any CLI context and any command:
<role name="admin">
<context-filters>
<context-filter name="01" cli-context-predicate="%" granted-commands="%"/>
</context-filters>
</role>Limited Admin Rights
This role grants full rights on any CLI context excluding the JMS Swiftlet and allows to save the router configuration, reboot a router (reboot% matches also for the HA commands rebootactive, rebootstandby), and to change property values (set):
<role name="admin">
<context-filters>
<context-filter name="01" cli-context-predicate="%" granted-commands="save% reboot% set"/>
<context-filter name="02" cli-context-predicate="/sys$jms%" type="exclude"/>
</context-filters>
</role>Operator Rights
This role is a typical operator role and assigned to the user anonymous which is the JMS user if no user name is used, thus a typical public role.
Filter
01uses CLI context/router1. This is a special context and is used to grant commands from the router node. Here it grants thesavecommand.Filter
02grants to view the collect interval property but marks it as read-only (although it is not). This is only for this user.Filter
03grants thenewcommand to create queues.Filter
04grants to view all declared queues and to change any property by granting thesetcommand for this context.Filter
05grants to view the usage section of the Queue Manager Swiftlet but only themessagecountproperty.
<role name="anonymous">
<context-filters>
<context-filter name="01" cli-context-predicate="/router1"
granted-commands="save"/>
<context-filter name="02" cli-context-predicate="/sys$queuemanager/collect-interval"
read-only="true"/>
<context-filter name="03" cli-context-predicate="/sys$queuemanager/queues"
granted-commands="new"/>
<context-filter name="04" cli-context-predicate="/sys$queuemanager/queues/%"
granted-commands="set"/>
<context-filter name="05" cli-context-predicate="/sys$queuemanager/usage/%/messagecount"/>
</context-filters>
</role>Enabling JMX (Java Management Extensions)
The Management Swiftlet of a SwiftMQ Router provides JMX support by wrapping the router's management tree with MBeans and thus exposing the management tree with all attributes and operations via a standard JMX interface.
Because creating and maintaining hundreds of dynamic MBeans consumes resources, JMX support is disabled by default. Enabling JMX requires that the SwiftMQ Router runs with JDK 1.5 or above. To enable JMX, set the attribute enabled of entity jmx to true:
<swiftlet name="sys$mgmt">
<jmx enabled="true" />
</swiftlet>This can be done in the routerconfig.xml before router startup or dynamically via SwiftMQ Explorer/CLI.
JMX must further be enabled on the JVM level by specifying the following system properties:
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=8999
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=falseThe port and whether to use JMX via SSL, with/without authentication is configurable, of course. Please consult the JMX documentation for further information.
The router is now manageable with your favorite JMX management tool.
Object Names
SwiftMQ's management tree is hierarchical. Some JMX management tools like jConsole are able to group MBeans if the MBean's object name contains a hierarchy within their key=value pairs. The content of the MBean's object name can be controlled via attribute groupable-objectnames of entity jmx. If set to true (default), an object name is grouped by using node and a sequence number as the key name. The following example shows a groupable object name of entity /sys$queuemanager/queues/testqueue:
com.swiftmq.router1:node0=sys$queuemanager, node1=queues, node2=testqueueAs shown, the JMX domain name is always com.swiftmq. appended with the router name.
Appearance in jConsole with grouped object names:
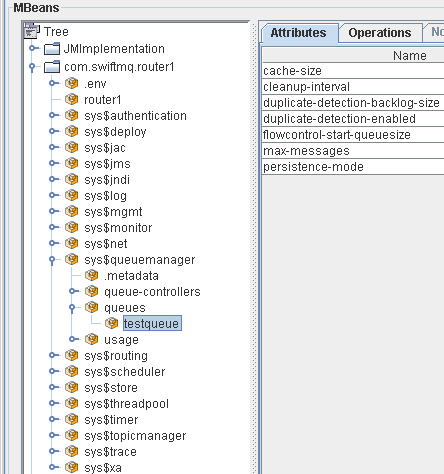
If attribute groupable-objectnames is set to false, the object names are flat and equal to the CLI context names:
com.swiftmq.router1:type=/sys$queuemanager/queues/testqueueExample to configure flat object names:
<swiftlet name="sys$mgmt">
<jmx enabled="true" groupable-objectnames="false"/>
</swiftlet>Appearance in jConsole with flat object names:
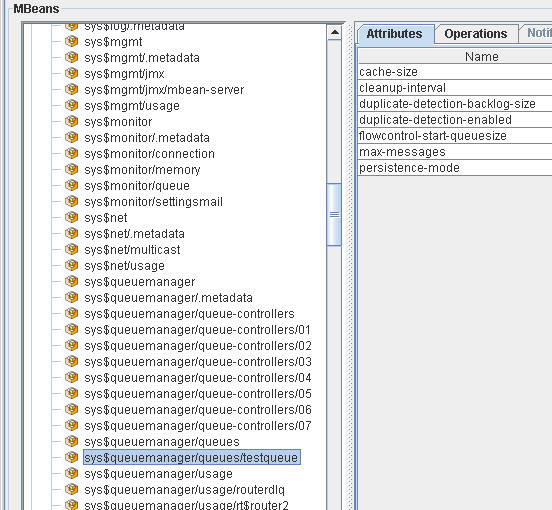
MBean Server
MBeans are registered at an MBean server. SwiftMQ registers its MBeans per default at the platform MBean server. However, it can also be configured to register at another one or even create a new one. This is controlled via entity mbean-server which is a sub-entity of jmx.
Example to use a named MBean server:
<swiftlet name="sys$mgmt">
<jmx enabled="true">
<mbean-server usage-option="use-named-server" server-name="SwiftMQ" />
</jmx>
</swiftlet>If the named MBean server is not defined, it is created and a message is logged to the warning.log.
Example to create a named MBean server:
<swiftlet name="sys$mgmt">
<jmx enabled="true">
<mbean-server usage-option="create-named-server" server-name="SwiftMQ" />
</jmx>
</swiftlet>Configuration
The configuration of the Management Swiftlet is defined within the element
<swiftlet name="sys$mgmt" .../>of the router's configuration file.
Attributes of Element "swiftlet"
Definition
Attribute | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
authentication-enabled | java.lang.Boolean | No | Enables/Disables Authentication |
admin-roles-enabled | java.lang.Boolean | No | Enables/Disables Administration Roles |
admintool-connect-logging-enabled | java.lang.Boolean | No | Enables/Disables Connect/Disconnect Logging of Admin Tools |
crfactory-class | java.lang.String | No | Challenge/Response Factory Class |
password | java.lang.String | No | Authentication Password |
flush-interval | java.lang.Long | No | Interval in which the Event queue is flushed to the SwiftMQ Explorers |
Values
Attribute | Values |
|---|---|
authentication-enabled | Default: false |
admin-roles-enabled | Default: false |
admintool-connect-logging-enabled | Default: true |
crfactory-class | Default: com.swiftmq.auth.ChallengeResponseFactoryImpl |
password | |
flush-interval | Min: 500 |
Element "jmx", Parent Element: "swiftlet"
JMX Settings.
Definition
Attribute | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
enabled | java.lang.Boolean | No | Enables/Disabled JMX Administration |
groupable-objectnames | java.lang.Boolean | No | Creates groupable Objectnames instead of flat Names |
Values
Attribute | Values |
|---|---|
enabled | Default: false |
groupable-objectnames | Default: true |
Element "mbean-server", Parent Element: "jmx"
MBean Server.
Definition
Attribute | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
usage-option | java.lang.String | No | How to use the MBean Server |
server-name | java.lang.String | No | MBean Server Name |
Values
Attribute | Values |
|---|---|
usage-option | Choice: use-platform-server use-named-server create-named-server |
server-name |
Element "message-interface", Parent Element: "swiftlet"
Message Interface Settings.
Definition
Attribute | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
enabled | java.lang.Boolean | No | Enables/Disabled Administration via Message Interface |
request-queue-name | java.lang.String | No | Input Queue Name for Admin Requests |
Values
Attribute | Values |
|---|---|
enabled | Default: false |
request-queue-name | Default: swiftmqmgmt-message-interface |
Element List "roles", Parent Element: "swiftlet"
Administration Roles. This element list contains zero or more "role" elements with this template definition:
Definition
Attribute | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name | java.lang.String | Yes | Name of this Role |
Element List "context-filters", Parent Element: "role"
CLI Context Filters. This element list contains zero or more "context-filter" elements with this template definition:
Definition
Attribute | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name | java.lang.String | Yes | Name of this Context Filter |
type | java.lang.String | No | Filter Type |
cli-context-predicate | java.lang.String | Yes | CLI Context Predicate (SQL Predicate) |
read-only | java.lang.Boolean | No | Is Read Only |
granted-commands | java.lang.String | No | Granted Commands of this CLI Context (SQL Like Predicates) |
Values
Attribute | Values |
|---|---|
type | Choice: include exclude |
cli-context-predicate | |
read-only | Default: false |
granted-commands |
Element List "usage", Parent Element: "swiftlet"
Connected Administration Tools. This element list contains zero or more "usage" elements with this template definition:
Definition
Attribute | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
name | java.lang.String | Yes | Name of this Connected Administration Tool |
hostname | java.lang.String | No | Host Name |
toolname | java.lang.String | No | Tool Name |
connecttime | java.lang.String | No | Connect Time |
lease-timeout | java.lang.String | No | Lease Timeout |
Values
Attribute | Values |
|---|---|
hostname | |
toolname | |
connecttime | |
lease-timeout |
